1. Creating our list of subdomains
Intro
Now that we know why we need to know subdomain enumeration, we need to string it all together to create a list of subdomains that we can use in further steps, but we need to make some attunements along the way. Some tools grab more subdomains than others, some are faster than others. We want to use them all! Yes that's right, as many tools as possible. The bigger our list of subdomains the better.
We will be using the following tools but please note that these are not the only tools by far. Our friends at https://pentester.land/ have done an amazing job setting up a cheat sheet for you that you can find here: https://pentester.land/cheatsheets/2018/11/14/subdomains-enumeration-cheatsheet.html#online-tools
While this is an EXCELLENT resource, it orders the tools alphabetically which is not the best approach for a course. We are going to chain together all these tools in an order that we need.
Installation and usage
Amass
First we needs brew. I'm going to assume you are all working on a linux machine or OSX machine, if not, you can download WSL.
/bin/bash -c "$(curl -fsSL https://raw.githubusercontent.com/Homebrew/install/HEAD/install.sh)"Sometimes the installation might give you an error:
Warning: /home/linuxbrew/.linuxbrew/bin is not in your PATH.
Make sure you do the following:
export PATH=$PATH:/home/linuxbrew/.linuxbrew/binIf your path is different, ofcourse change it.
Now we can finally run brew to install amass
brew tap caffix/amass
brew install amassDNSRecon
wget https://github.com/darkoperator/dnsrecon/archive/refs/heads/master.zip
cd dnsrecon-master/
sudo python3 setup.py install
pip3 install -r requirements.txt
IF you get an error:
WARNING: The script netaddr is installed in '/home/USER/.local/bin' which is not on PATH.
Then you need to:
export PATH=$PATH:/home/USER/.local/binAltDNS
pip install py-altdnsUsing the tools
Amass
Intell is the option where we use Amass to Perform OSINT for us. We have several options available to use such as running the found results through a reverse whois domain.
Simple Enum:
amass enum -d example.com >> domains-google.com.txt
Intel:
amass intel -org google
This will result in CIDR records:
amass intel -ip -src -cidr IP.IP.IP.IP >> domains-google.com.txttesThe >> will send the subdomains to a file
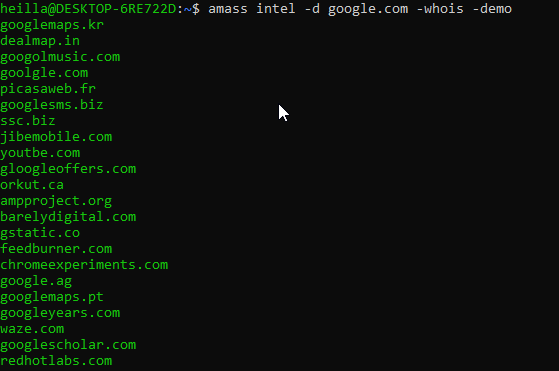
We also have the enum mode where amass will enumerate a lot of subdomains.
amass enum -d google.com >> domains-google.com.txtWe can also add the passive flag to force off passive scans
amass enum-d owasp.org -passive >> domains-google.com.txtAmass has a lot more flags an options that i encourage you to look at!
https://github.com/OWASP/Amass/blob/master/doc/user_guide.md
Certificate transparency automation
Our good friends over at "The art of subdomain enumeration" have forseen several scripts to helps us scrape the websites that have been made available to us:
https://github.com/appsecco/the-art-of-subdomain-enumeration
sudo apt-get install unzip
sudo apt install python-pip
wget https://github.com/appsecco/the-art-of-subdomain-enumeration/archive/refs/heads/master.zip
unzip master.zip
cd the-art-of-subdomain-enumeration-master
pip install -r requirements.txtDNSRecon
We need to first change into the directory that we downloaded dnsrecon into. Ones there, we can run the DNSRecon tool with python 3.6+
python3 dnsrecon.py -d google.com -D subdomains-top1mil-5000.txt -t brtSeveral wordlists are included with DNSRecon but it pays off to learn how to create your own that's tuned to your target.
- D will tell DNSRecon which list of subdomains to use
- t type of resolution to try
Possible types: std: SOA, NS, A, AAAA, MX and SRV. rvl: Reverse lookup of a given CIDR or IP range. brt: Brute force domains and hosts using a given dictionary. srv: SRV records. axfr: Test all NS servers for a zone transfer. bing: Perform Bing search for subdomains and hosts. yand: Perform Yandex search for subdomains and hosts. crt: Perform crt.sh search for subdomains and hosts. snoop: Perform cache snooping against all NS servers for a given domain, testing all with file containing the domains, file given with -D option.
AltDNS
We need to generate a new list of subdomains and try to resolve them.
- i A list of know subdomains that altDNS uses to create it's permutations from
- o The output
- r altDNS will try to resolve all the generated domains
- s The output of the resolution of the generated domains
./altdns.py -i known-subdomains.txt -o new_subdomains.txt -r -s domains-google.com.AltDNS.txtFinishing touches
We can run other tools like SubFinder, FinDomain, dnssearch,... to complete our list, for those see the github pages. (See List of tools for those). We also need to merge all our lists and remove any duplicates we have in there.
We need to also make sure none of these subdomains containt a protocol (http:// or https://), the tool we will use in the next step will be adding that automatically.
Results
We are now left with a GIANT file that contains a list of subdomains, but we are not even sure if they are alive so we will need to check which domains are actually useful to us.