IDOR
What is it
IDOR: Insecure Direct Object Reference
These types of vulnerabilities arise from acces control issues. We will devote another entire chapter to those types of vulnerabilities. The term IDOR was made popular in by appearing in the OWASP top 10 but in reality it's simply another type of Broken Access Control issue. IDORs can manifest in both horizontal and vertical privilege escalation. To speak of an IDOR, the following conditions have to be met:
- An object identifier exists in the request, either as GET or POST parameter
- A Broken Access Control issue has to exist allowing the user access to data they should not be able to access
These terms may seem abstract so let's look at an example:
- GET /invoice.php?id=12
- POST /personalInfo.php
- {personId:23,name:"tester"}
- GET /invoices/1234.txt
In these examples we can see a POST and a GET request being made, both contain an identifier. In a normal situation, the user can only access invoices or personal data that belong to them. If we however change this identifier and get data returned that does not belong to our user, we have an IDOR.
This may seem like a simple interpretation of IDORs, but this is basically how it works. The complexity comes from how we can automate looking for this and from the different users in involved.
Attack strategy
We can basically take a manual or semi-automated strategy for this.
Manually
Manually searching for IDORs is probably the easiest way. In a previous chapter we went over your main attack strategy. This stated that you should explore the website with your MitM proxy in the background. (See general attack strategy). Burp suite has an option to show parameterised requests:
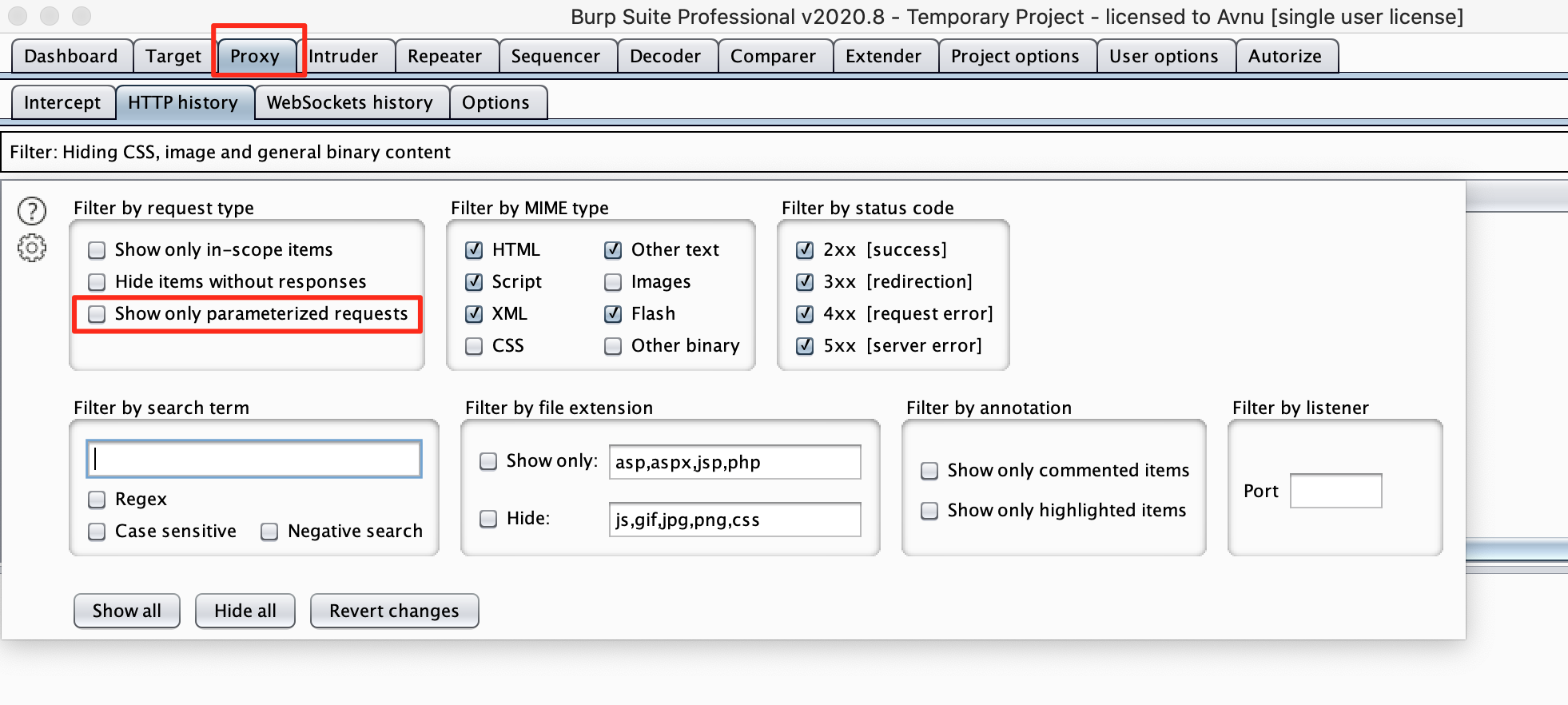
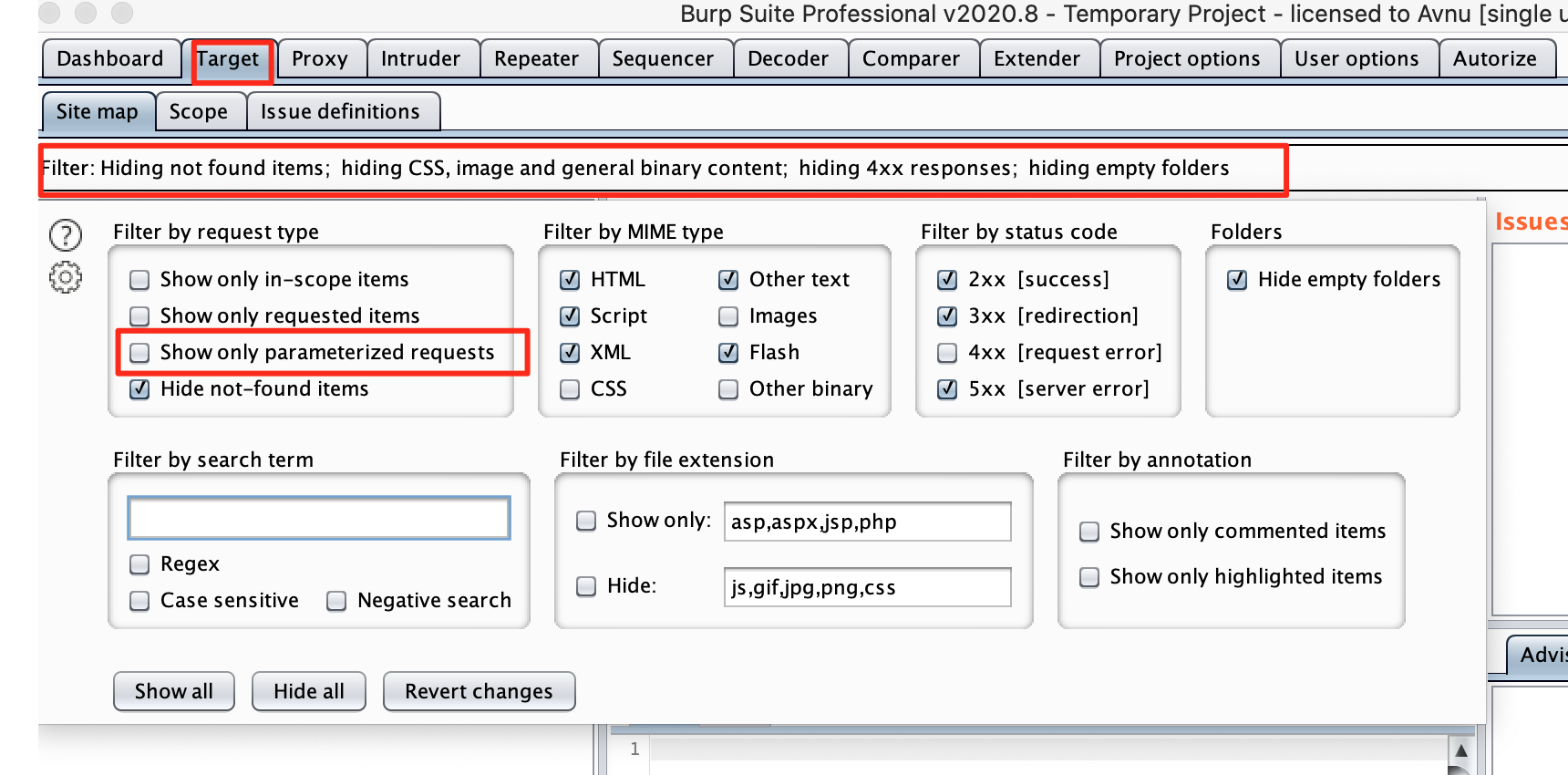
We can use this filter to show us any request that contains parameters. We will have to go through these requests manually and send the requests that contain identifiers to the repeater.
In the repeater we can replace the authentication methods the are expected by the server with some valid authentication tokens.
- JWT in authorisation header might need to be replaced
- Session cookies might need to be replaced
- Custom authentication methods may be in place
You will need to identify which authentication mechanism is being used and make sure you replace any expired authentication methods with valid ones. Grab new valid tokens by logging in and making similar requests.
Now that you have the request working in the repeater, we can try replacing the identifiers in the request.
BE CAREFUL: You are a bug bounty hunter, you are testing a live production environment. Do not fill in a random identifier. Instead create a new account. Log into that account and navigate to the same functionality.
Example:
- We have a request going to GET /invoice.php?id=12
- Send it to the repeater
- The request contains a JWT token in the authorization header that is expired
- When you launch the request, it will return a 500 because the JWT is expired
- Log in to the application and check the http history in your proxy tab
- One of the latest requests should contain a JWT token that's valid
- Copy that JWT token
- Replace the expired JWT token in your repeater
- You should get a 200 OK response from the server now
- Create a new account
- Log into that account and check the http history in your proxy tab
- One of the latest requests should contain a JWT token that's valid
- Copy that JWT token
- Replace the JWT token in your repeater
- If you are now receiving a 200 OK response from the server AND the content of the invoice, you have an IDOR
Semi-automated testing
Authorize
Please refer to Tools > Burp Authorize
Match and replace
Please refer to Tools > Burp: Match and replace